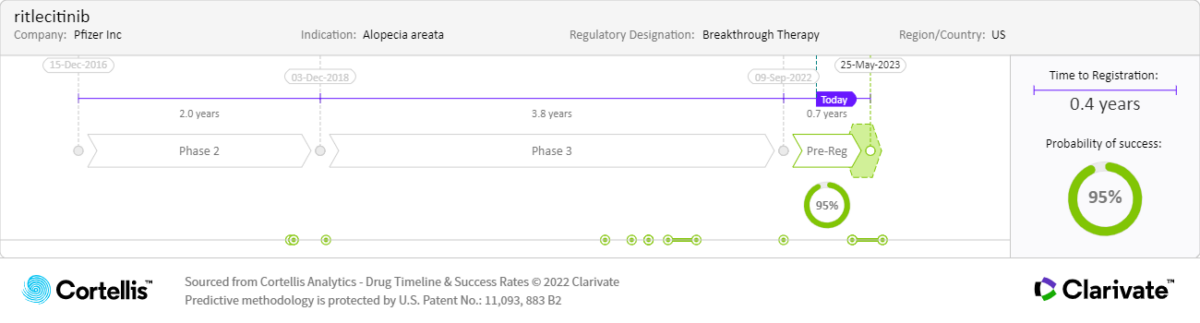
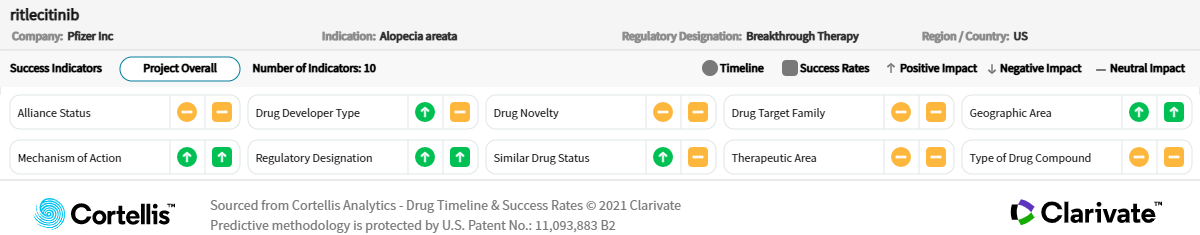
About ritlecitinib
-
Pfizer Inc
-
Janus kinase 3 (JAK3)/TEC inhibitor Daily oral administration to treat alopecia areata
-
Also being evaluated for vitiligo, Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis and, in combination with either tofacitinib or zimlovisertib, rheumatoid arthritis
-
~4.7 million people with alopecia areata in the United States and top five European markets in 2020